Introduction
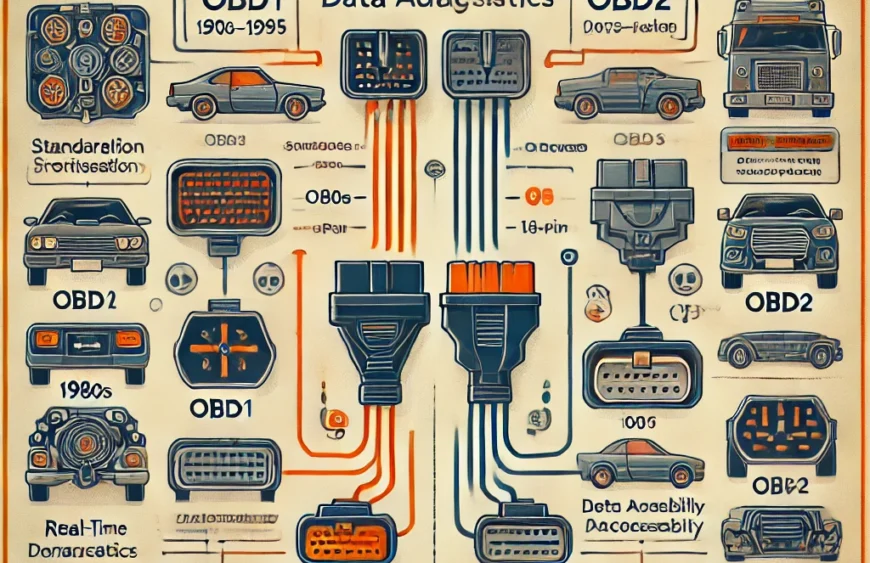
On-Board Diagnostics, commonly known as OBD, revolutionized how we maintain and repair vehicles. These systems monitor vital engine and emissions functions, providing crucial data to mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike. Over time, two major diagnostic standards emerged — OBD1 and OBD2 — each with unique strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding the key differences between OBD1 vs OBD2 is essential whether you own a classic car or a modern vehicle. In this guide, we break down the history, features, advantages, and practical implications of both systems.
What is OBD1?
Introduced in the late 1980s and early 1990s, OBD1 was the first generation of vehicle diagnostics. Designed primarily for emission control, OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific — meaning each brand (Honda, Ford, GM, etc.) developed its own unique setup.
While groundbreaking for its time, OBD1 had major limitations: limited data output, minimal standardization, and difficulty accessing or interpreting codes without special tools.
What is OBD2?
OBD2 replaced OBD1 starting in 1996 in the United States, bringing a universal standard across all manufacturers.
With OBD2, any compliant scanner could access the vehicle’s diagnostics, covering a wide range of systems beyond emissions — including transmission, airbags, ABS, and more.
OBD2 also introduced real-time data streaming, making it easier to monitor performance and diagnose problems quickly.
OBD1 vs OBD2: Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Year Introduced | 1980s – Early 1990s | 1996 onwards |
| Compatibility | Manufacturer-specific | Universal across brands |
| Diagnostic Access | Requires special tools and procedures | Standardized OBD-II port |
| Data Monitored | Limited (mostly emissions) | Comprehensive (engine, transmission, ABS, etc.) |
| Emissions Compliance | Early-stage emissions control | Mandatory emissions standards |
| Live Data Availability | Minimal or none | Full real-time data streaming |
| Readable with Generic Scanners | No | Yes |
| Code Standardization | Manufacturer-specific codes | Standardized plus OEM-specific codes |
| Example Vehicles | 1992 Honda Civic, 1994 Chevy Blazer | 1997 Toyota Camry, 2015 Ford Mustang |
✅ As you can see, OBD2 dramatically improves functionality and accessibility compared to OBD1.
Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
1. Standardization
- OBD1: Custom protocols per manufacturer (very confusing!)
- OBD2: Single standardized protocol (SAE J1962) across all makes and models.
2. Coverage
- OBD1: Focused mainly on emissions and basic engine faults.
- OBD2: Covers engine, transmission, ABS, airbags, climate control, and more.
3. Diagnostics Tools
- OBD1: Requires specific reader tools depending on the brand.
- OBD2: Works with any modern OBD-II scanner — plug and play!
4. Readability
- OBD1: Often needed to “jumper” pins and count dashboard flashes to interpret codes.
- OBD2: Instantly readable digital codes and live data via scanner.
5. Repair and Troubleshooting
- OBD1: More manual diagnosis, harder to pinpoint issues.
- OBD2: Fast, precise diagnostics and better repair strategies.
Real-World Example: Diagnosing an OBD1 vs OBD2 Vehicle
Imagine diagnosing a 1992 Honda Civic with an OBD1 system.
You’d need to manually jumper two pins under the dashboard and count how many times the check engine light flashes — one flash, pause, two flashes, etc. (complicated and error-prone!).
In contrast, diagnosing a 2010 Ford Focus (OBD2) simply involves connecting a handheld scanner to the OBD-II port under the steering column, pressing a button, and instantly reading trouble codes with full descriptions.
👉 OBD2 saves time, reduces guesswork, and improves accuracy.
What About EOBD and EOBD2?
You might also encounter the terms EOBD and EOBD2:
- EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics) is Europe’s version of OBD2, mandatory for petrol vehicles from 2001 and diesel from 2004.
- EOBD2 isn’t an official new standard — it’s often used informally to describe newer vehicles or software updates based on the EOBD framework.
In practice, EOBD = OBD2 for European models.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
The main difference is that OBD1 is manufacturer-specific and limited mainly to emissions, while OBD2 is universal across brands, offering comprehensive system diagnostics and real-time data.
Can you use an OBD2 scanner on an OBD1 car?
No. OBD2 scanners are not compatible with OBD1 systems unless a manufacturer-specific adapter and software are used — and even then, coverage is limited.
What year did cars switch from OBD1 to OBD2?
In the United States, 1996 was the official transition year when all cars and light trucks were required to use OBD2.
Is OBD2 better than OBD1?
Yes. OBD2 offers standardized diagnostics, easier access to data, broader system coverage, and greater efficiency in identifying and fixing vehicle problems.
Are all OBD2 ports the same?
Yes. All OBD2 ports use the same 16-pin connector, typically located under the dashboard, making diagnostics simple and universal.
Conclusion
Both OBD1 and OBD2 played pivotal roles in vehicle diagnostics history, but there’s no doubt that OBD2 offers superior ease, coverage, and accuracy.
Understanding the difference between OBD1 vs OBD2 ensures you choose the right tools and techniques when maintaining or repairing vehicles — saving time, money, and frustration.
For professional-grade OBD2 scanners and tools, explore our full range at Techroute66.com 🚗.